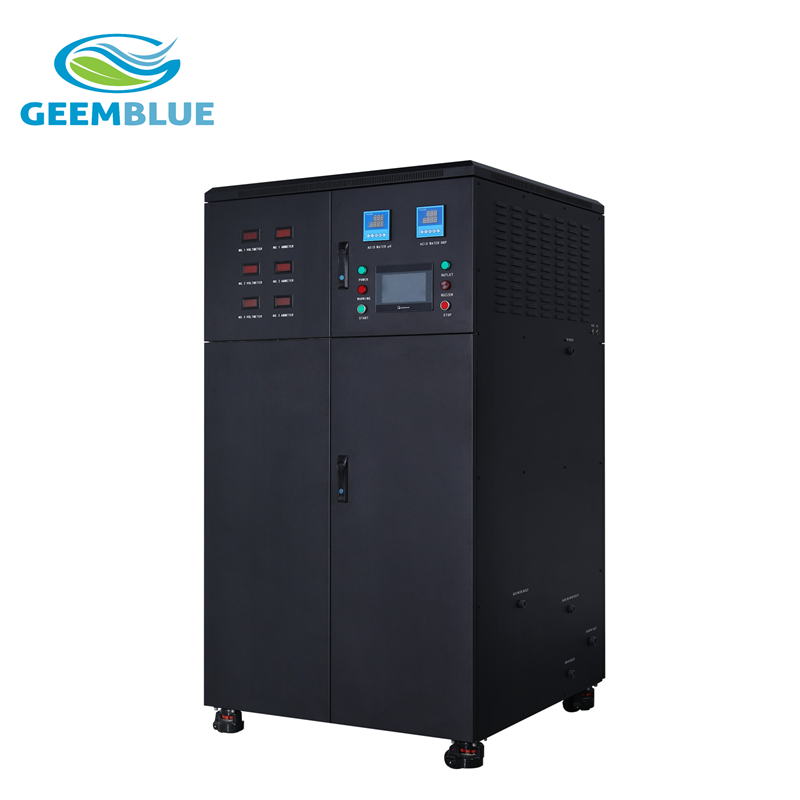
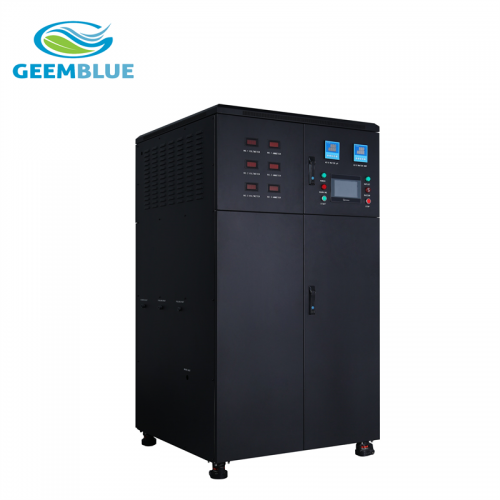
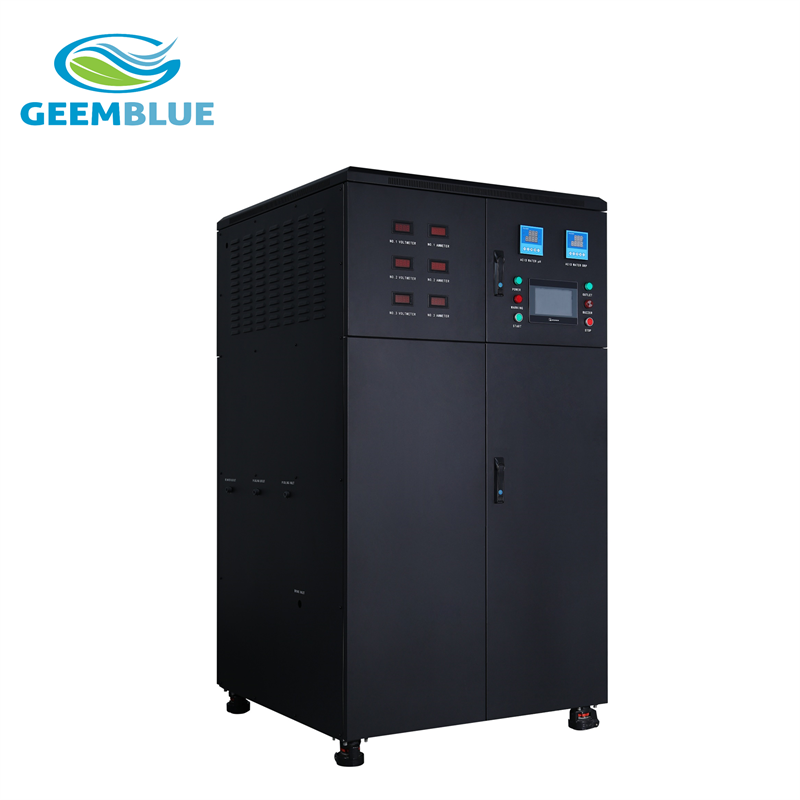
GBA-400L-HCLO
PARAMETERS
Ph range: 3~8
Orp: 800~1100mV
Additives: Softened salt
Salt consumption: 5g per liter HOCl
Water Consumption: 1.35L per liter HOCl
Po
Introduction
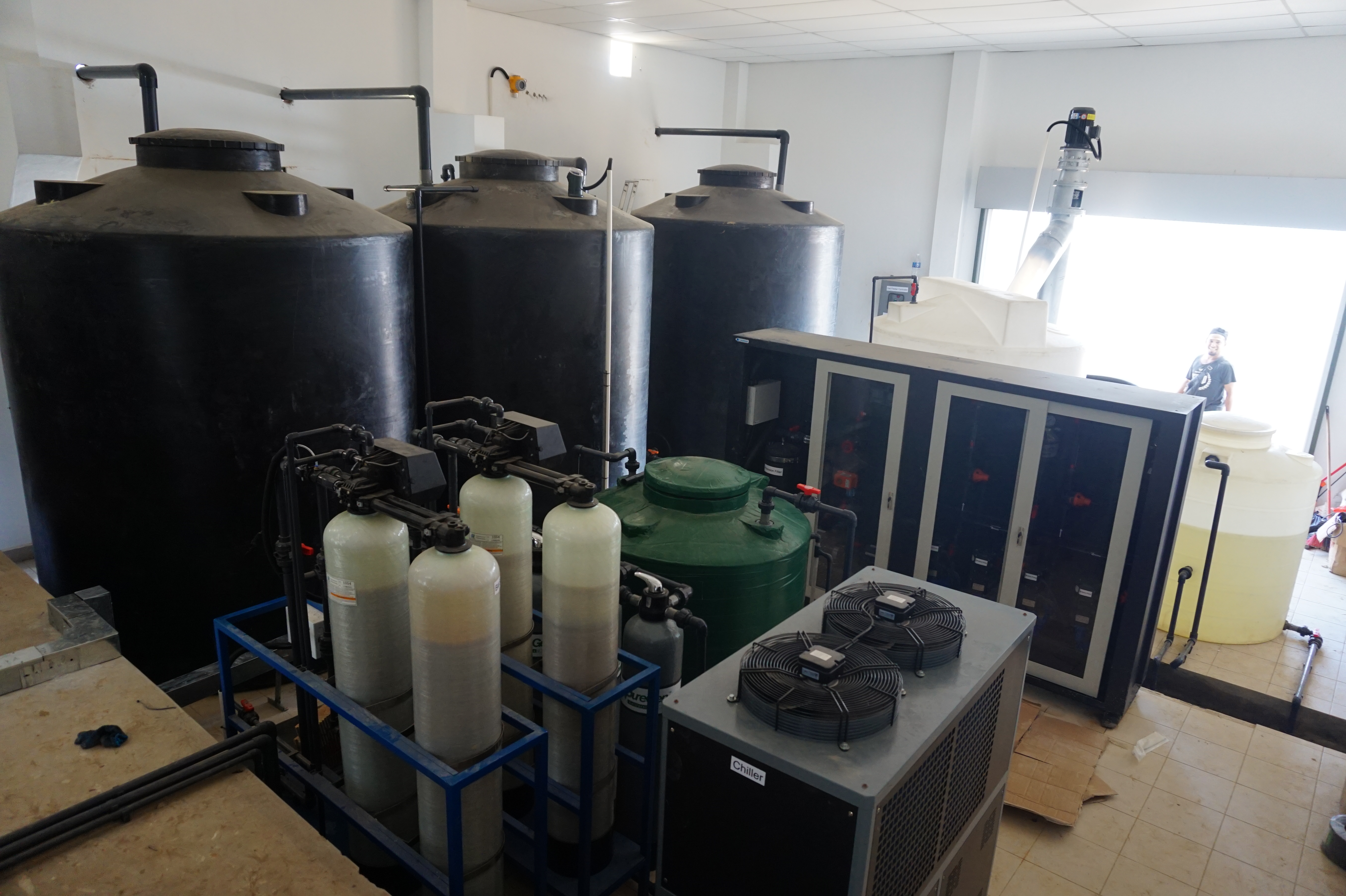
Hypochlorous acid generator is a system which is produced by electrolysis of tap water through water purification system and is produced by a special electrolytic cell. The system produce hypochlorous acid (HCLO) with pH (3~8), redox potential (ORP value +800mv or more) and available chlorine (up to 800ppm), also produce sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with PH (10~12), redox potential(ORP value -800~900 mv).
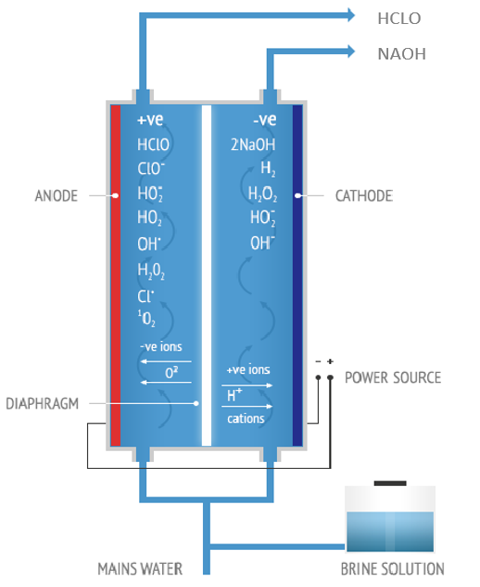
Principle of electrolysis
Hypochlorous acid generator electrolyzes 0.3% of NaCl solution in a special electrolytic module. In the advanced anion membrane, the acid oxidation potential water is generated from the anode side and the alkaline reduction potential is generated from the cathode side. Most of the alkaline water will enter the anode chamber twice, and after the second electrolysis, the slightly acidic electrolytic ion water will be generated from the anode side. A small amount of alkaline water will be generated from cathode side.
Technical principle
Anolyte from anode
The slightly acidic water (HOCl) produced from anode side with high redox potential and excellent germicidal ability, and it contains no chemical additives. The slightly acidic electrolyzed water is a solution with high safety, no residue and environmentally friendly.
Catholyte from cathode
The main component of catholyte is sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with 10~12 PH, -800~900mv ORP, which can effectively clean and disinfect the general surface, activate crop growth, or as a coagulation or flocculant (handling mild heavy metal pollution, or ingesting oily ingredients in the isolation solution, etc.), even replacing iodine to clean the wound, or properly adjust pH of liquid, etc.
When to use it
| Where Used | Effect |
| Sterilizing cut vegetables | After cleaning, vegetables are sanitized and kept fresh for longer time: crisp and crunchy. |
| Sterilizing & sanitizing cutting board | The cutting board cleaned with Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water can be kept clean without bacteria growth. |
| Hygienic management of pool | Used for the water in public pools, it has outstanding sterilization effect and allows much reduced chlorine odor compared with the conventional sterilization method. |
| Sterilization and sanitization of plant facilities | It is time-proven with more than 10 year`s experiences including large milk plants in Japan. |
Sterilization effect
| Bacterial | Before Treatment[cfu/ml] | After Treatment[Time] |
| S.aureus subsp.aureus IFO12732 | 1.8*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Yersinia enterocolitica IID981 | 4.8*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Campylobacter coli ATCC33559 | 4.0*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Campylovacter jejuni subsp.jejuni ATCC33560 | 6.0*107 | - (30 sec) |
| Salmonella enteritidis IFO3313 | 2.1*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Escherichia coli ATCC43895 O157:H7 | 5.2*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Listeria monocytogenes VTU206 | 2.5*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Serratia marcescens IFO12648 | 2.9*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO13275 | 3.7*108 | - (30 sec) |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD2210100 | 3.1*108 | - (1 min) |
| Clostridium boturinum A CB21 | 2.6*104 | - (1 min) |
Effective chlorine concentration 10 ppm, treated at 20
(reference : Microbes Sterilization Practical Data/Sciience Forum Inc.)
Sterilization methods comparison
| Item | Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water | Sodium Hypochlorite | Heat Sterilization |
| Sporular Sterilization | Can be sterilized | Can hardly be sterilized | Can hardly be sterilized (<100℃) |
| Odor-causing Incident | None | Possible | None |
| Wasted Water | None | Flushing water | Cooling Water |
| Wasted Time | None | Flushing period | Cooling Period |
| Energy Cost | Minimun | Minimum | Extra heating energy required |
| Waste water Treatment | No effect | Significantly affected. Pre-treatment & reserve tank required. | No effect |
| Equipment Damage | None | Corrodes equipment when concentrated. | Rapid temperature change will expand and contract equipment., which could cause crack and eventually pollution. |
| Hazardous Material | None | Possible contamination with chloric acid & bromic acid Trihalomethane could be produced. | None |
| Operational Safety | Dangerous |
Application of HClO